Chevrolet Trax: Diagnostic information and procedures
SYMPTOMS - ENGINE MECHANICAL
Strategy Based Diagnostics
Perform a Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle .
All diagnosis on a vehicle should follow a logical process. Strategy based diagnostics is a uniform approach for repairing all systems. The diagnostic flow may always be used in order to resolve a system condition. The diagnostic flow is the place to start when repairs are necessary.
Visual/Physical Inspection
- Inspect for aftermarket devices which could affect the operation of the engine.
- Inspect the easily accessible or visible system components for obvious damage or conditions which could cause the symptom.
- Inspect for the correct oil level, proper oil viscosity, and correct filter application.
- Verify the exact operating conditions under which the concern exists. Note factors such as engine RPM, ambient temperature, engine temperature, amount of engine warm-up time, and other specifics.
- Compare the engine sounds, if applicable, to a known good engine and make sure you are not trying to correct a normal condition.
Intermittent
Test the vehicle under the same conditions that the customer reported in order to verify the system is operating properly.
Symptom List
Refer to a symptom diagnostic procedure from the following list in order to diagnose the symptom:
- Base Engine Misfire without Internal Engine Noises
- Base Engine Misfire with Abnormal Internal Lower Engine Noises
- Base Engine Misfire with Abnormal Valve Train Noise
- Base Engine Misfire with Coolant Consumption
- Base Engine Misfire with Excessive Oil Consumption
- Engine Noise on Start-Up, but Only Lasting a Few Seconds
- Upper Engine Noise, Regardless of Engine Speed
- Lower Engine Noise, Regardless of Engine Speed
- Engine Noise Under Load
- Engine Will Not Crank - Crankshaft Will Not Rotate
- Engine Compression Test
- Oil Consumption Diagnosis
- Oil Pressure Diagnosis and Testing
- Drive Belt Chirping, Squeal, and Whine Diagnosis
- Drive Belt Rumbling and Vibration Diagnosis
- Drive Belt Falls Off and Excessive Wear Diagnosis
OIL PRESSURE DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Special Tools
- EN-498-B Oil Pressure Gauge
- EN-498-3 Adapter
For equivalent regional tools, refer to Special Tools.
Removal Procedure
- Disconnect the oil pressure indicator switch wiring harness plug.
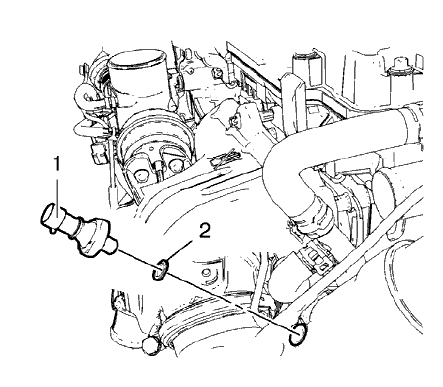
Fig. 12: Engine Oil Pressure Indicator Switch
- Remove the oil pressure indicator switch (1) and the oil pressure indicator switch seal ring (2).
Measuring Procedure
.gif)
Fig. 13: Gauge And Adapter
- Install EN-498-B gauge (1) along with EN-498-3 adapter (2).
- Start Engine.
NOTE: The oil temperature should be between 80ºC (176ºF)and 100ºC (212º).
- Measure the oil pressure:
- The oil pressure at idle speed should be 150 kpa (22 psi).
- The oil pressure between 3000 - 3500 rpmshould be 380 - 650 kpa (55 - 94 psi).
- Stop engine.
- If the engine oil pressure is below specifications, inspect the engine for 1 or more of the following conditions:
- Oil pump worn or dirty. Refer to Oil Pump Replacement, and Engine Front Cover and Oil Pump Cleaning and Inspection.
- Oil suction gallery clogged or dirty. Refer to Oil Pan Cleaning and Inspection
- Cracked, porous, or restricted oil galleries.
- Oil pressure relief valve malfunction.
- Remove EN-498-B gauge and EN-498-3 adapter.
Installation Procedure
.gif)
Fig. 14: Engine Oil Pressure Indicator Switch
- Install the oil pressure indicator switch (1) and a NEW oil pressure indicator switch seal ring (2).
CAUTION: Refer to Fastener Caution .
- Tighten the oil pressure indicator switch to 20 N.m (15 lb ft).
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Oil Leak Diagnosis
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
OIL CONSUMPTION DIAGNOSIS
Oil Consumption Diagnosis
.jpg)
.jpg)
ENGINE NOISE UNDER LOAD
Engine Noise Under Load
.jpg)
ENGINE NOISE ON START-UP, BUT ONLY LASTING A FEW SECONDS
Engine Noise on Start-Up, but Only Lasting a Few Seconds
.jpg)
BASE ENGINE MISFIRE WITHOUT INTERNAL ENGINE NOISES
Base Engine Misfire without Internal Engine Noises
.jpg)
.jpg)
BASE ENGINE MISFIRE WITH ABNORMAL INTERNAL LOWER ENGINE NOISES
Base Engine Misfire with Abnormal Internal Lower Engine Noises
.jpg)
.jpg)
BASE ENGINE MISFIRE WITH ABNORMAL VALVE TRAIN NOISE
Base Engine Misfire with Abnormal Valve Train Noise
.jpg)
BASE ENGINE MISFIRE WITH COOLANT CONSUMPTION
Base Engine Misfire with Coolant Consumption
.jpg)
BASE ENGINE MISFIRE WITH EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
Base Engine Misfire with Excessive Oil Consumption
.jpg)
UPPER ENGINE NOISE, REGARDLESS OF ENGINE SPEED
Upper Engine Noise, Regardless of Engine Speed
.jpg)
LOWER ENGINE NOISE, REGARDLESS OF ENGINE SPEED
Lower Engine Noise, Regardless of Engine Speed
.gif)
.jpg)
ENGINE WILL NOT CRANK - CRANKSHAFT WILL NOT ROTATE
Engine Will Not Crank - Crankshaft Will Not Rotate
.jpg)
.jpg)
ENGINE COMPRESSION TEST
Special Tools
EN-48248 Cylinder Compression Pressure Gauge
For equivalent regional tools, refer to Special Tools.
Removal Procedure
- Remove the throttle body assembly. Refer to Throttle Body Assembly Replacement .
- Remove the spark plugs. Refer to Spark Plug Replacement .
- Remove the relay holder cover.
- Remove the fuel pump relay.
NOTE: The engine cranking time for the compression test should be less then 10 seconds and at 30 second intervals.
- Crank the engine with the starter motor for 5 seconds to remove any foreign substances from the cylinders.
- Prior to taking a compression reading, verify the cranking speed is greater than 300 RPM. If the cranking speed is below 300 RPM, repair the slow cranking speed condition before continuing with the compression test.
- Install EN-48248 gauge in the spark plug bore for the cylinder that is being checked.
- Using the vehicle's starter motor, rotate or crank the engine for 4 compression strokes, puffs, for the cylinder being tested.
- Observe the compression gauge and note the reading as the compression test is being performed. A normal cylinder reading will be indicated if compression builds up quickly and evenly to the specified level. An abnormal reading will be indicated if compression is low on the first compression stroke, starts increasing on the following compression strokes but does not reach the specified level.
- Record the compression reading for the cylinder just tested.
- Repeat steps for all remaining cylinders. All 4 cylinders must be tested to obtain valid test results. Record the readings.
- The maximum pressure differential should not exceed 100 kPa (14.5 psi).
- The nominal cylinder compression value is
- for natural aspirated engines 1300 kPa - 1500 kPa (188.5 psi - 217.6 psi).
- for turbo engines 1200 kPa - 1400 kPa (174 psi - 203.1 psi).
Installation Procedure
- Install the fuel pump relay.
- Install the relay holder cover.
- Install the spark plugs. Refer to Spark Plug Replacement .
- Install the throttle body assembly. Refer to Throttle Body Assembly Replacement .
DRIVE BELT CHIRPING, SQUEAL, AND WHINE DIAGNOSIS
Diagnostic Aids
- A chirping or squeal noise may be intermittent due to moisture on the
drive belts or the pulleys. It may be
necessary to spray a small amount of water on the drive belts in order to
duplicate the customers concern.
If spraying water on the drive belt duplicates the symptom, cleaning the belt pulleys may be the probable solution.
- If the noise is intermittent, verify the accessory drive components by varying their loads making sure they are operated to their maximum capacity. An overcharged A/C system, power steering system with a pinched hose or wrong fluid, or a generator failing are suggested items to inspect.
- A chirping, squeal or whine noise may be caused by a loose or improper
installation of a body or
suspension component. Other items of the vehicle may also cause the noise.
The drive belts will not cause a whine noise.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
2
The noise may not be engine related. This step is to verify that the engine is making the noise. If the engine is not making the noise do not proceed further with this table.
3
The noise may be an internal engine noise. Removing the drive belts one at a time and operating the engine for a brief period will verify the noise is related to the drive belt. When removing the drive belt the water pump may not be operating and the engine may overheat. Also DTCs may set when the engine is operating with the drive belts removed.
4
Inspect all drive belt pulleys for pilling. Pilling is the small balls or pills or it can be strings in the drive belt grooves from the accumulation of rubber dust.
6
Misalignment of the pulleys may be caused from improper mounting of the accessory drive component, incorrect installation of the accessory drive component pulley, or the pulley bent inward or outward from a previous repair. Test for a misaligned pulley using a straight edge in the pulley grooves across two or three pulleys. If a misaligned pulley is found refer to that accessory drive component for the proper installation procedure for that pulley.
10
Inspecting of the fasteners can eliminate the possibility that a wrong bolt, nut, spacer, or washer was installed.
12
Inspecting the pulleys for being bent should include inspecting for a dent or other damage to the pulleys that would prevent the drive belt from not seating properly in all of the pulley grooves or on the smooth surface of a pulley when the back side of the belt is used to drive the pulley.
14
This test is to verify that the drive belt tensioner operates properly. If the drive belt tensioner is not operating properly, proper belt tension may not be achieved to keep the drive belt from slipping which could cause a squeal noise.
15
This test is to verify that the drive belt is not too long, which would prevent the drive belt tensioner from working properly. Also if an incorrect length drive belt was installed, it may not be routed properly and may be turning an accessory drive component in the wrong direction.
16
Misalignment of the pulleys may be caused from improper mounting of the accessory drive component, incorrect installation of the accessory drive component pulley, or the pulley bent inward or outward from a previous repair. Test for a misaligned pulley using a straight edge in the pulley grooves across two or three pulleys. If a misaligned pulley is found refer to that accessory drive component for the proper installation procedure for that pulley.
17
This test is to verify that the pulleys are the correct diameter or width. Using a known good vehicle compare the pulley sizes.
19
Replacing the drive belt when it is not damaged or there is not excessive pilling will only be a temporary repair.
Drive Belt Chirping, Squeal, and Whine Diagnosis
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
DRIVE BELT RUMBLING AND VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
Diagnostic Aids
The accessory drive components can have an affect on engine vibration. Vibration from the engine operating may cause a body component or another part of the vehicle to make rumbling noise. Vibration can be caused by, but not limited to the A/C system over charged, the power steering system restricted or the incorrect fluid, or an extra load on the generator. To help identify an intermittent or an improper condition, vary the loads on the accessory drive components.
The drive belt may have a rumbling condition that can not be seen or felt. Sometimes replacing the drive belt may be the only repair for the symptom.
If replacing the drive belt, completing the diagnostic table, and the noise is only heard when the drive belts are installed, there might be an accessory drive component with a failure. Varying the load on the different accessory drive components may aid in identifying which component is causing the rumbling noise.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
2
This test is to verify that the symptom is present during diagnosing. Other vehicle components may cause a similar symptom.
3
This test is to verify that one of the drive belts is causing the rumbling noise or vibration. Rumbling noise may be confused with an internal engine noise due to the similarity in the description. Remove only one drive belt at a time if the vehicle has multiple drive belts. When removing the drive belts the water pump may not be operating and the engine may overheat. Also DTCs may set when the engine is operating with the drive belts removed.
4
Inspecting the drive belts is to ensure that they are not causing the noise. Small cracks across the ribs of the drive belt will not cause the noise. Belt separation can be recognized at the edge of the belt or felt as a lump in the belt.
5
Small amounts of pilling is normal condition and acceptable. When the pilling is severe the drive belt does not have a smooth surface for proper operation.
9
Inspecting of the fasteners can eliminate the possibility that the wrong bolt, nut, spacer, or washer was installed.
11
This step should only be performed if the water pump is driven by the drive belt. Inspect the water pump shaft for being bent. Also inspect the water pump bearings for smooth operation and excessive play.
Compare the water pump with a known good water pump.
12
Accessory drive component brackets that are bent, cracked, or loose may put extra strain on that accessory component causing it to vibrate.
Drive Belt Rumbling and Vibration Diagnosis
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
DRIVE BELT FALLS OFF AND EXCESSIVE WEAR DIAGNOSIS
Diagnostic Aids
If the drive belt repeatedly falls off the drive belt pulleys, this is because of pulley misalignment.
An extra load that is quickly applied on released by an accessory drive component may cause the drive belt to fall off the pulleys. Verify the accessory drive components operate properly.
If the drive belt is the incorrect length, the drive belt tensioner may not keep the proper tension on the drive belt.
Excessive wear on a drive belt is usually caused by an incorrect installation or the wrong drive belt for the application.
Minor misalignment of the drive belt pulleys will not cause excessive wear, but will probably cause the drive belt to make a noise or to fall off.
Excessive misalignment of the drive belt pulleys will cause excessive wear but may also make the drive belt fall off.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
2
This inspection is to verify the condition of the drive belt. Damage may of occurred to the drive belt when the drive belt fell off. The drive belt may of been damaged, which caused the drive belt to fall off. Inspect the belt for cuts, tears or sections of ribs missing.
4
Misalignment of the pulleys may be caused from improper mounting of the accessory drive component, incorrect installation of the accessory drive component pulley, or the pulley bent inward or outward from a previous repair. Test for a misaligned pulley using a straight edge in the pulley grooves across two or three pulleys. If a misaligned pulley is found refer to that accessory drive component for the proper installation procedure of that pulley.
5
Inspecting the pulleys for being bent should include inspecting for a dent or other damage to the pulleys that would prevent the drive belt from not seating properly in all of the pulley grooves or on the smooth surface of a pulley when the back side of the belt is used to drive the pulley.
6
Accessory drive component brackets that are bent or cracked will let the drive belt fall off.
7
Inspecting of the fasteners can eliminate the possibility that a wrong bolt, nut , spacer, or washer was installed. Missing. loose, or the wrong fasteners may cause pulley misalignment from the bracket moving under load. Over tightening of the fasteners may cause misalignment of the accessory component bracket
13
The inspection is to verify the drive belt is correctly installed on all of the drive belt pulleys. Wear on the drive belt may be caused by mis-positioning the drive belt by one groove on a pulley.
14
The installation of a drive belt that is two wide or two narrow will cause wear on the drive belt. The drive belt ribs should match all of the grooves on all of the pulleys.
15
This inspection is to verify the drive belt is not contacting any parts of the engine or body while the engine is operating. There should be sufficient clearance when the drive belt accessory drive components load varies. The drive belt should not come in contact with an engine or a body component when snapping the throttle.
Drive Belt Falls Off and Excessive Wear Diagnosis
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
DRIVE BELT TENSIONER DIAGNOSIS
Special Tools
EN-48488 Holding Wrench
For equivalent regional tools, refer to Special Tools.
- Diagnosis consists of a function check on the automatic belt tensioner and a visual check on the belt and the components linked to the belt.
.gif)
Fig. 15: Drive Belt Tensioner Spring, Drive Belt Tensioner Pulley Bolt And
Wrench
- Install the EN-48488 wrench (2) to the drive belt tensioner pulley bolt (1).
- Apply tension to the drive belt tensioner spring (3) by moving the drive belt tensioner pulley clockwise.
- Allow the drive belt tensioner to slide back slowly and thereby inspect the drive belt tensioner mechanism for practicability.

