Chevrolet Trax: Brake rotor surface and wear inspection
WARNING: Refer to Brake Dust Warning .
- If the inboard friction surface of the brake rotor is not accessible, reposition and support the caliper with the brake pads. Refer to Front Disc Brake Pads Replacement.
- Clean the friction surfaces of the brake rotor with denatured alcohol, or an equivalent approved brake cleaner.
- Inspect the friction surfaces of the brake rotor for the following braking surface conditions:
- Heavy rust and/or pitting
Light surface rust can be removed with an abrasive disc. Heavy surface rust and/or pitting must be removed by refinishing the brake rotor.
- Cracks and/or heat spots
- Too much blueing discoloration
- If the friction surfaces of the brake rotor exhibit one or more of the braking surface conditions, the brake rotor requires refinishing or replacement.
.gif)
Fig. 3: Micrometer On Brake Rotor
- Using a micrometer (1) calibrated in thousandths-of-a-millimeter, or ten-thousandths-of-an-inch, measure and record the scoring depth of any grooves present on the brake rotor friction surfaces.
- Compare the groove scoring depth recorded to the following specification:
Specification
Brake rotor maximum allowable scoring: 1.50 mm (0.059 in) .
- If the brake disc rotor scoring depth exceeds the specification, or if an excessive amount of scoring is present, the brake rotor requires refinishing or replacement.
BRAKE ROTOR ASSEMBLED LATERAL RUNOUT MEASUREMENT
Special Tools
- CH-41013 Rotor Surfacing Kit
- CH-42450-A Wheel Hub Resurfacing Kit
- CH-45101 Hub and Wheel Runout Gauge
- CH-45101-100 Conical Brake Rotor Washers
For equivalent regional tools, refer to Special Tools.
WARNING: Refer to Brake Dust Warning .
NOTE:
- Brake rotor assembled lateral runout (LRO) exceeding the maximum allowable specification can cause thickness variation to develop in the brake rotor over time, usually between 4,800-11,300 km (3,000- 7,000 mi).
- Brake rotor thickness variation MUST be inspected BEFORE
inspecting for assembled lateral runout (LRO). Thickness variation
exceeding the maximum acceptable level can cause brake pulsation.
Refer to Brake Rotor Thickness Variation Measurement.
- Matchmark the position of the brake rotor to the wheel studs if this has not been done already.
NOTE: Whenever the brake rotor has been separated from the hub/axle flange, any rust or contaminants should be cleaned from the hub/axle flange and the brake rotor mating surfaces. Failure to do this may result in excessive assembled lateral runout (LRO) of the brake rotor, which could lead to brake pulsation.
- Inspect the mating surface of the hub/axle flange and the brake rotor to make sure that there are no foreign particles, corrosion, rust, or debris remaining. If the wheel hub/axle flange and/or brake rotor mating surfaces exhibit these conditions, perform the following steps:
- Remove the brake rotor from the vehicle. Refer to Front Brake Rotor Replacement.
- Using the CH-42450-A wheel hub resurfacing kit , thoroughly clean any rust or corrosion from the mating surface of the hub/axle flange.
- Using the CH-41013 rotor resurfacing kit , thoroughly clean any rust or corrosion from the mating surface of the brake rotor.
- Clean the friction surfaces of the brake rotor with denatured alcohol, or an equivalent approved brake cleaner.
- Install the rotor to the hub/axle flange using the matchmark made prior to removal.
.gif)
Fig. 4: One Lug Nut & Conical Brake Rotor Washers
- Hold the brake rotor firmly in place against the hub/axle flange and install one of the CH-45101-100 conical brake rotor washers (1), and one lug nut (2) onto the upper-most wheel stud.
- Continue to hold the brake rotor secure and tighten the lug nut firmly by hand.
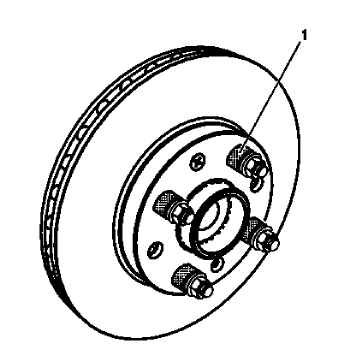
Fig. 5: Wheel Studs
- Install the remaining CH-45101-100 conical brake rotor washers (1) and lug nuts onto the wheel studs and tighten the nuts firmly by hand in the tightening sequence.
- Tighten the lug nuts in sequence, in order to properly secure the rotor. Refer to Tire and Wheel Removal and Installation .
- If the brake rotor has been REFINISHED or REPLACED with a new rotor, proceed to step 14.
- If the brake rotor meets the following criteria, proceed to step 10.
- The rotor is within specifications and is being REUSED.
- The rotor has NOT been refinished.
- The rotor does not exhibit thickness variation exceeding the maximum allowable level.
.gif)
Fig. 6: Hub And Wheel Runout Gauge
- Mount a dial indicator, CH-45101 hub and wheel runout gauge (1), or equivalent, to the steering knuckle and position the indicator button so it contacts the brake rotor friction surface at a 90 degree angle, approximately 13 mm (0.5 in) from the outer edge of the rotor.
- Measure and record the assembled LRO of the brake rotor:
- Rotate the rotor until the lowest reading is displayed on the indicator dial, then set the dial to zero.
- Rotate the rotor until the highest reading is displayed on the dial.
- Mark the location of the high spot relative to the nearest wheel stud, or studs.
- Measure and record the amount of assembled LRO.
- Compare the brake rotor assembled LRO to the following specification:
Specification
Front brake rotor maximum allowable assembled lateral runout: 0.05 mm (0.002 in)
- If the brake rotor assembled LRO is within specifications, proceed to step 18.
If the brake rotor assembled LRO exceeds the specification, refinish the rotor to ensure true parallelism.
Refer to Brake Rotor Refinishing. After refinishing the rotor, proceed to step 14.
- Mount a dial indicator, CH-45101 hub and wheel runout gauge , or equivalent, to the steering knuckle and position the indicator button so it contacts the brake rotor friction surface at a 90 degree angle, approximately 13 mm (0.5 in) from the outer edge of the rotor.
- Measure and record the assembled LRO of the brake rotor.
- Rotate the rotor until the lowest reading is displayed on the indicator dial, then set the dial to zero.
- Rotate the rotor until the highest reading is displayed on the dial.
- Mark the location of the high spot relative to the nearest wheel stud, or studs.
- Measure and record the amount of assembled LRO.
- Compare the brake rotor assembled LRO to the following specification:
Specification
Front brake rotor maximum allowable assembled lateral runout: 0.05 mm (0.002 in) .
- If the brake rotor assembled LRO measurement exceeds the specification, bring the LRO to within specifications. Refer to Brake Rotor Assembled Lateral Runout Correction.
- If the brake rotor assembled LRO measurement is within specification, install the brake caliper and depress the brake pedal several times to secure the brake rotor in place before removing the CH-45101- 100 conical brake rotor washers and the lug nuts.

